Database Structure Design
Database Structure
The "Synmetrix" database is organized according to the relational database model and includes the following tables:
public.users: Stores information about registered users, including user ID (id), display name (display_name), avatar URL (avatar_url), as well as the creation time and last update time of the record.
auth.account_providers: Describes the relationships between user accounts and their authentication providers.
auth.accounts: Stores information about user accounts, including unique identifiers, email addresses, passwords, and other data.
auth.providers: Provides a list of available authentication providers.
auth.refresh_tokens: Contains information about refresh tokens for each user account.
auth.roles: Manages user roles.
auth.account_roles: Contains information about roles for each account.
public.teams: Stores information about user teams.
public.datasources: Contains information about data sources used by users.
public.dataschemas: Describes data models used to define business metrics for data sources.
public.explorations: Describes research tasks performed by users.
public.members: Stores information about team members.
public.team_roles: Manages user roles within teams.
public.member_roles: Contains information about roles for each team member.
public.reports: Contains information about the structure and schedule of reports based on metrics needed by users.
public.sql_credentials: Manages SQL credentials used to access business metrics through the SQL interface.
public.alerts: Stores information about alerts created by users.
Database Architecture Description
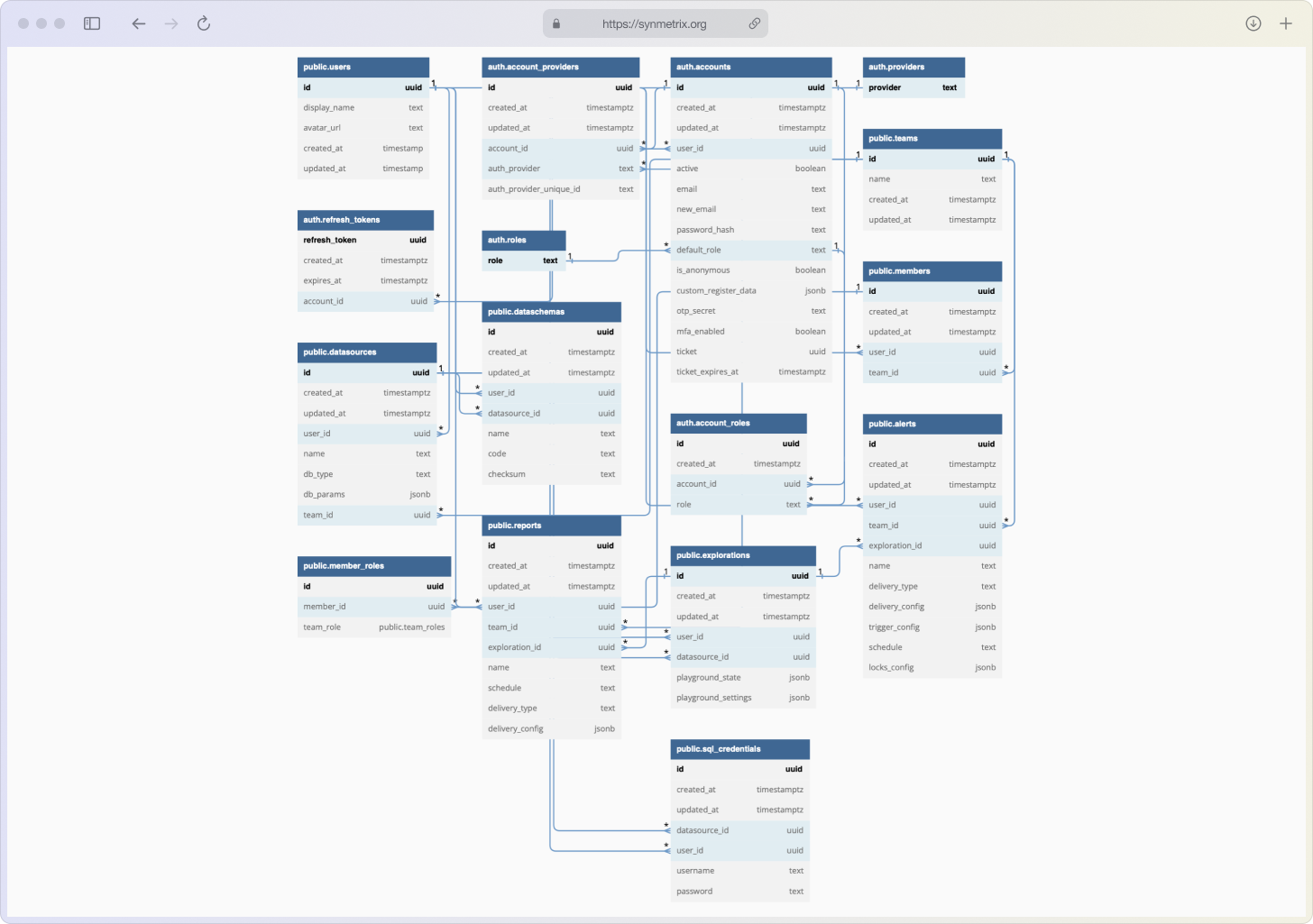
The architecture of the database, including relationships between tables, primary and foreign keys, and indexes, is represented in the Database Markup Language (DBML).
This database structure provides flexibility and scalability to the system, allowing convenient management of users, teams, data sources, reports, and other system elements. Each database table is designed for a specific purpose and can be extended or modified to meet evolving system requirements.